Smart competition can shape shared progress

As China is about to adopt the 15th Five-Year Plan (2026-30), a critical transformation is unfolding: its manufacturing sector is advancing toward higher intelligence, more digitalization, and high-end development. This development reflects not only China's own ambition for innovation-driven growth but also signals a broader shift in the global industrial landscape.
At this pivotal moment, how China and the United States — two economic giants and manufacturing powerhouses — manage their competition and seek avenues for cooperation will shape the future of global supply chains, economic stability and technological progress.
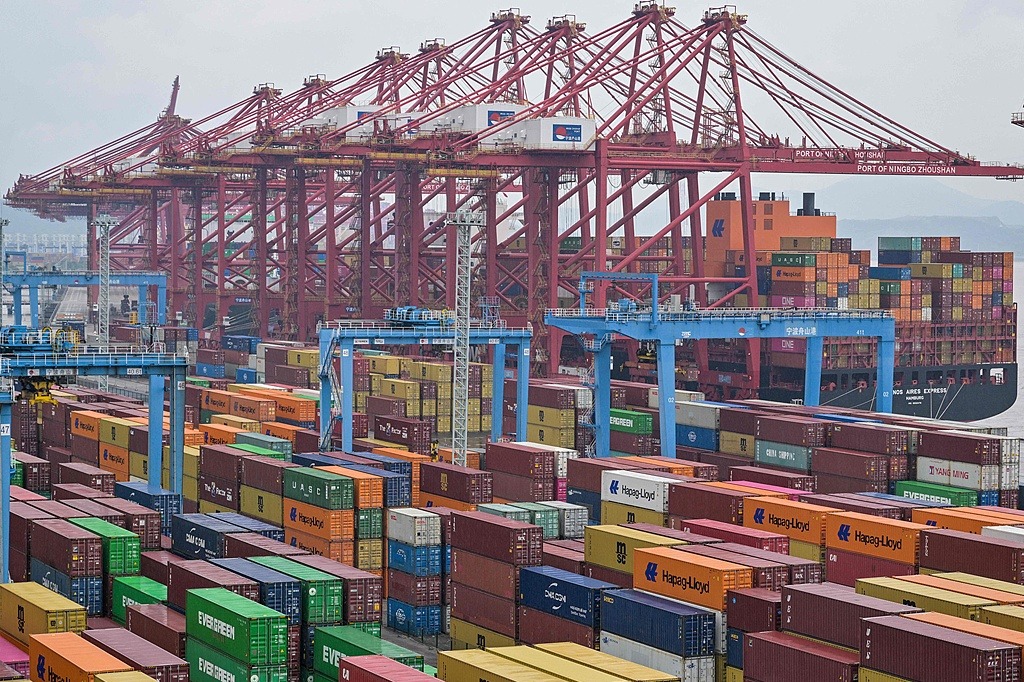
The international environment has become more uncertain. Rising geopolitical tensions, protectionist policies, and growing anti-globalization sentiments have tested the resilience of global supply chains. As the world grapples with climate change, inflation and high-tech disruption, the world is desperately in need of stability and cooperation. And yet calls for "decoupling" and strategic containment threaten to derail decades of interconnected development.
China and the US are still interdependent. In manufacturing alone, their collaboration fuels innovation, scale and efficiency across electronics, clean energy, aerospace, smart devices, automotive and other sectors. While both sides understandably seek to enhance domestic resilience and sharpen their competitive edge, it would be a mistake to turn healthy competition into zero-sum confrontation. Managed correctly, competition can coexist with cooperation; and in manufacturing, it must.
To help achieve China's manufacturing goals, the 15th Five-Year Plan will likely focus on advancing "new quality productive forces", which include artificial intelligence, advanced robotics, green energy systems, and industrial internet platforms. The goal is to move beyond low-cost mass production and build a more agile, intelligent and globally integrated industrial base. This is not a departure from globalization, but an upgrade, one that is already attracting investments, talents and collaboration from across the world.
The US is also pursuing a manufacturing renaissance, investing in domestic semiconductor and battery production sectors, and taking measures for "reshoring" high-tech industries through legislation such as the CHIPS and Science Act during the previous term of the Joe Biden administration. While it is natural for a country to secure critical capabilities, it is equally important to acknowledge that no country alone can shape the future of manufacturing.
Since supply chains are no longer national but global, digital and deeply collaborative, China and the US should identify sectors of shared interests, instead of disengaging. Green manufacturing is one such sector. Both sides have committed to reducing carbon emissions and building sustainable industries. Cooperation in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy components and smart grid infrastructure can help expedite innovation and improve global standards to the benefit of all. Likewise, digital transformation in manufacturing — where China's edge in industrial scale meets the US' strength in software — offers natural synergy.
Collaboration is not about dependency. It is about interdependence with mutual respect. Chinese and US enterprises are already working together across complex supply chains, from design and prototyping to logistics and assembly. Rather than dismantling these ecosystems, the need is to make them more resilient, transparent and sustainable. Joint research centers, cross-border industrial parks, and open innovation platforms are all ways to deepen trust while maintaining competitive vitality.
However, it is crucial to resist seeing every aspect of US-China economic relations through the lens of national security. While safeguarding core technologies is legitimate, the unfettered use of sanctions, tariffs and export controls risks dividing the global economy into rigid blocs. Such a division would slow innovation, raise costs, and hurt consumers and businesses on both sides.
Beyond economics, cooperation in manufacturing can have a stabilizing geopolitical effect — and shared industrial goals create opportunities for dialogue, talent exchange and mutual understanding. These create a practical, apolitical bridge — one that connects workers, engineers and entrepreneurs in pursuit of shared prosperity. Manufacturing is not only the backbone of national economies; it is also a foundation of international trust.
There is also a moral case for cooperation. With the world facing economic uncertainty and widening inequality, China and the US have a responsibility to promote inclusive growth, especially because developing countries depend on affordable, reliable manufacturing to build infrastructure, create employment, and alleviate poverty. If the world's two largest economies choose cooperation over confrontation, they can offer not just technologies, but hope as well.
It's time to reframe the US-China manufacturing narrative — not as a battle for supremacy, but as a race to create value, resilience and sustainability. Each country brings unique strength, but only together can they lead a new era of industrial progress — one defined not by who wins, but by what the world gains.
The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
The author is president of the America China Public Affairs Institute, an honorary fellow of the Foreign Policy Association, senior adviser to the China-United States Exchange Foundation, executive council member of the Center for China and Globalization, and visiting professor at the School of International Studies, Sichuan University.
Today's Top News
- Urban renewal beyond economic growth
- Xi meets Russian FM in Beijing
- Xi meets heads of foreign delegations attending SCO council of foreign ministers meeting
- Xi addresses Central Urban Work Conference, listing priorities for urban development
- China reports 5.3% GDP growth in H1
- China handles 95 billion parcels in first half of year